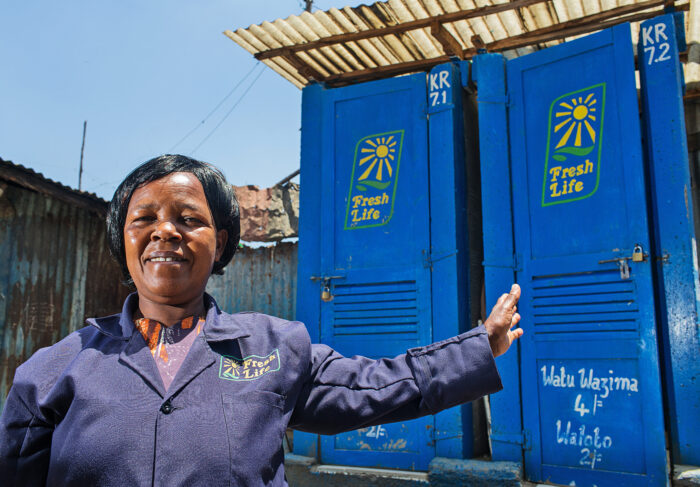
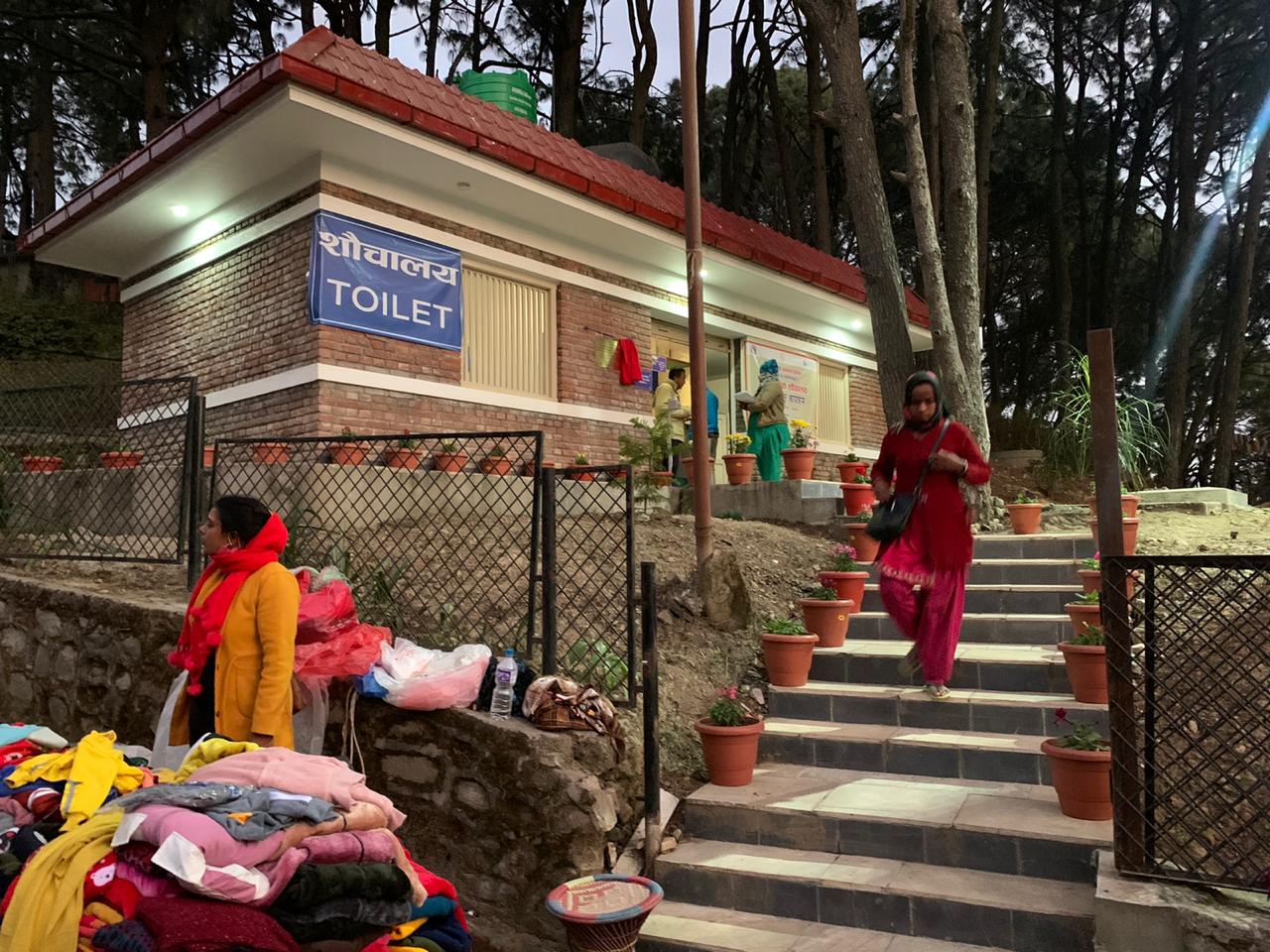
KATHMANDU, NEPAL — What if your morning tea was brewed using energy from a public toilet? Thanks to a clever Canadian-backed innovation, human waste is being transformed into clean energy that powers local tea shops, reduces pollution, and creates jobs.
Poor sanitation is a major challenge in Nepal, where over 10 million people lack access to improved facilities, according to UNICEF. Across Kathmandu, the country’s bustling capital, public toilets have long been unsafe, unhygienic, and inaccessible, especially for women and people with disabilities. Poor sanitation limits women’s mobility and participation in public life, while untreated waste seeps into rivers, threatening public health and the environment.
With support from Grand Challenges Canada (GCC) in partnership with the Government of Canada, Aerosan, a Halifax-based organization, is reshaping sanitation in two of Nepal’s biggest cities through their innovative solution: the Aerosan HUB.
The HUB Model: Turning Toilet Waste into Energy and Opportunity
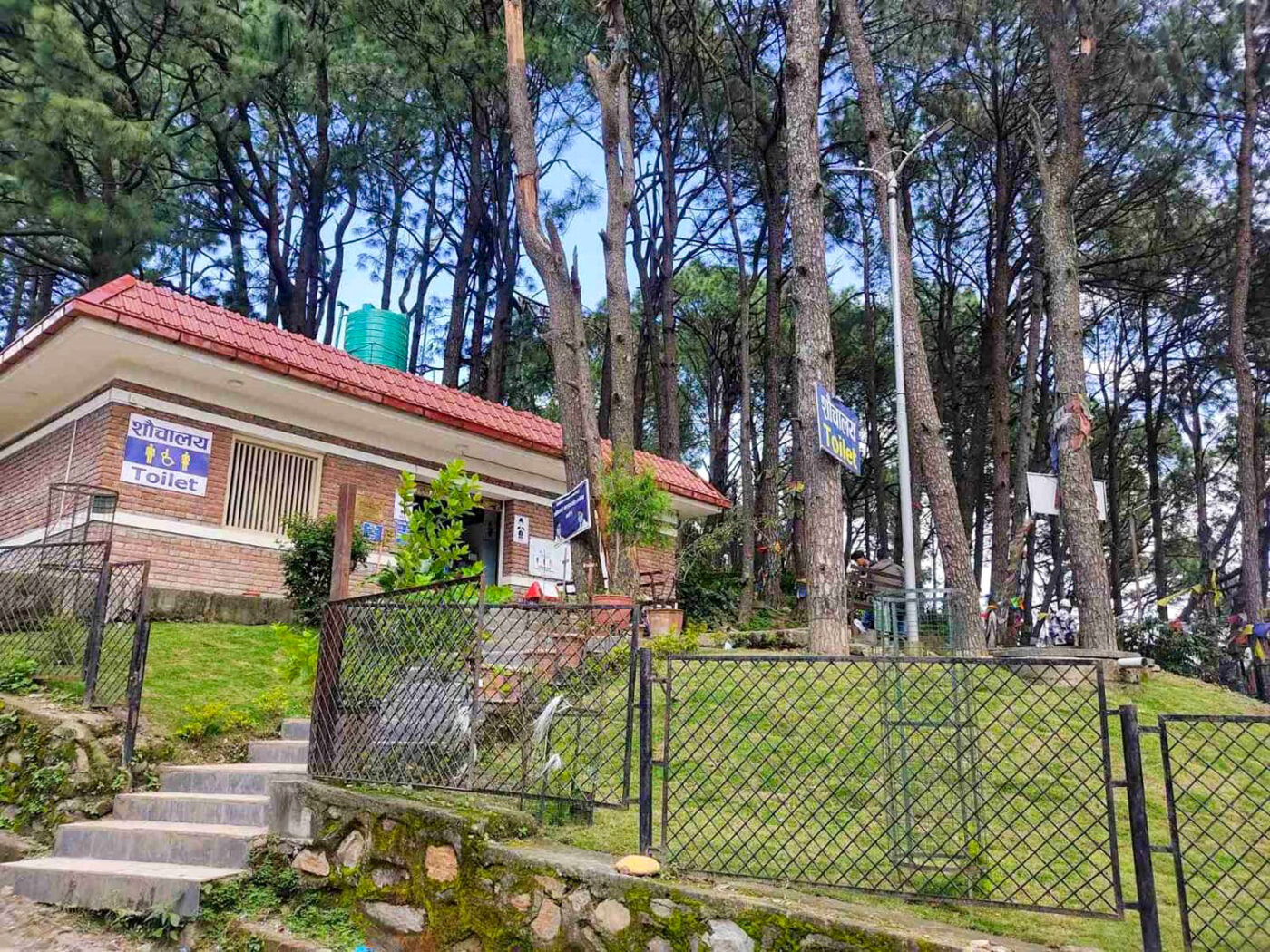

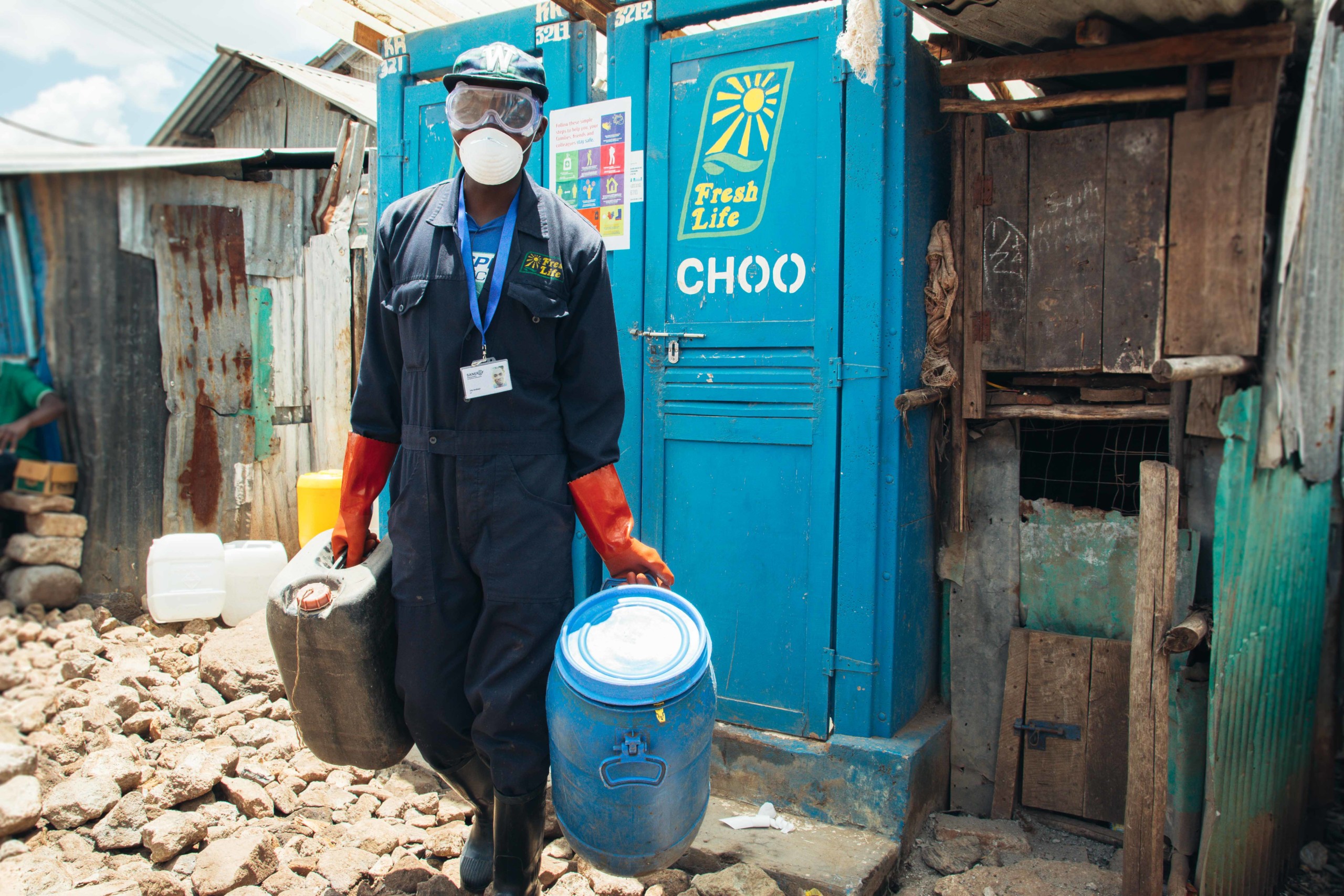
Each Aerosan toilet HUB serves as a sanitation site that blends smart design, clean energy, and social enterprise. It’s a model that goes beyond toilets: it’s about dignity, sustainability, and empowerment.
Every HUB includes:
- Gender-inclusive facilities designed for safety, privacy, and accessibility. They include segregated toilets and handwashing stations, access to clean water and menstrual hygiene products, and disposal bins to support menstrual hygiene management.
- On-site waste processing through an underground anaerobic digester, a sealed tank where microbes break down waste without oxygen to produce biogas, a clean and renewable energy source. The gas is then piped to nearby businesses, powering stoves and reducing reliance on costly and polluting liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
At one site in Kathmandu, a local tea shop now runs up to 16 hours a day using biogas produced from the HUB’s toilets. Meanwhile, wastewater is treated on-site, keeping around 40 tons of waste annually from entering local rivers and lakes.
As a pay-per-use sanitation model, each HUB generates sufficient revenue to cover its operating and maintenance costs. When combined with income from biogas energy sales and local business partnerships, the approach has proven to be both financially self-sustaining and community-owned.
The HUBs also create meaningful employment opportunities for sanitation workers, many from marginalized communities. Moreover, each facility is managed by a women-led cooperative that oversees daily operations and shares directly in the revenue, ensuring that economic empowerment remains at the heart of the model.
Scaling Innovation Through Partnerships
Aerosan’s success is rooted in collaboration. With early and ongoing investment from Grand Challenges Canada, they piloted and refined their HUB model in Nepal’s urban centers.GCC supports Aerosan with patient, flexible, blended funding, including grants and loans, that give the company room to experiment, learn, and refine its business model without the pressure of rigid financing. Partnership with local governments in Kathmandu and Lalitpur are a key feature of the model. The Hubs are built on land that is leased from the government, who also provide financial contributions for the physical infrastructure.

The results are tangible. Each Aerosan HUB serves between 150 and 200 people daily. Since implementation, and thanks to their inclusive design, women’s use of Aerosan facilities has increased by 46 percent—a critical step toward improving gender equity in public spaces.

The economic impact is equally significant. Biogas generation cuts energy costs for small businesses, while the creation of a cooperative with over 500 members is stimulating local economic growth and fostering entrepreneurship.
“Sanitation is often seen as a cost,” says an Aerosan representative. “But with the right approach, it becomes an engine for social and economic development.”
Today, Aerosan’s HUBs have delivered safe sanitation to more than 900,000 people—about one in every 30 Nepalis. With ambitions to expand to 60 sites and reach up to 3 million people, the initiative has the potential to become a national model for sustainable urban sanitation.
A Canadian-led model for the Future
The story of Aerosan underscores Canada’s growing role in driving innovation for sustainable development. Through Grand Challenges Canada, the Government of Canada supports bold ideas that deliver measurable health, economic, and environmental benefits around the world.
In 2023–24 alone, GCC invested $41 million in 88 innovations across 100 countries, spanning maternal and newborn health, mental health, sanitation, sexual and reproductive health, and humanitarian innovation. To date, we have funded projects that have reached over 85 million people and improved 28 million lives globally.
The partnership between Aerosan, local governments, and communities in Nepal shows how Canadian-supported innovation can drive change, and how even the most overlooked resource –human waste– can be transformed into energy, opportunity, and lasting impact.